Conception: How It Works
Conception (or fertilization) is when sperm and an egg join together. It’s one of the many steps that happen to create a pregnancy.
To become pregnant, these steps must occur:
- Sperm Transport: The sperm must be deposited and transported to the site of fertilization
- Egg Transport: Ovulation must occur and the egg must be “picked up” by the tube
- Fertilization and Embryo Development: Union between the sperm and egg must result
- Implantation: The embryo must implant and begin to grow in the uterus
Sperm Transport
The transport of sperm is dependent upon several factors. The sperm must be capable of propelling themselves through the environment of the female vagina and cervix. This environment, which is under cyclic hormonal control, must be favorable to admit the sperm without destroying them. Finally, the sperm must possess the capability of converting to a form that can penetrate the cell membrane of the egg (capacitation). Following ejaculation, the semen forms a gel which provides protection for the sperm from the acidic environment of the vagina. The gel is liquefied within 20-30 minutes by enzymes from the prostate gland. This liquefaction is important to free the sperm so transportation may occur. The seminal plasma is left in the vagina. The protected sperm with the greatest motility travel through the layers of cervical mucus that guard the entrance to the uterus. During ovulation, this barrier becomes thinner and changes its acidity creating a friendlier environment for the sperm. The cervical mucus acts as a reservoir for extended sperm survival. Once the sperm have entered the uterus, contractions propel the sperm upward into the fallopian tubes. The first sperm enter the tubes minutes after ejaculation. The first sperm, however, are likely not the fertilizing sperm. Motile sperm can survive in the female reproductive tract for up to 5 days.
Egg Transport
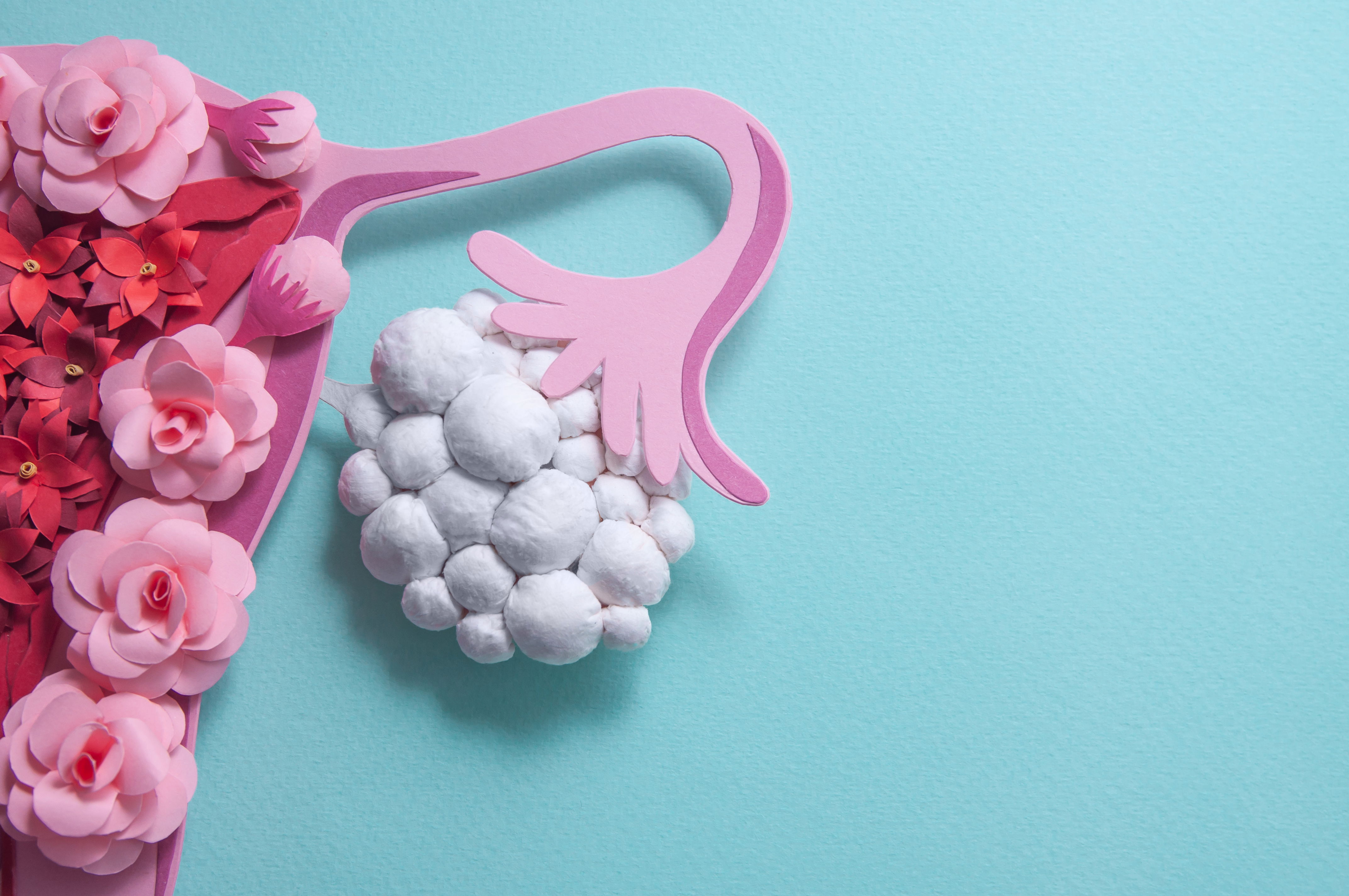

Egg transport begins at ovulation and ends once the egg reaches the uterus. Following ovulation, the fimbriated (finger-like) end of the fallopian tube sweeps over the ovary. Adhesive sites on the cilia, which are located on the surface of the fimbriae, are responsible for egg pickup and movement into the tube. The cilia within the tube and muscular contractions resulting from the movement of the egg create a forward motion. Transport through the tube requires about thirty hours. Conditions such as pelvic infections and endometriosis can permanently impair the function of the fallopian tubes, due to scarring and or damage to the fimbriae. Once the egg arrives at a specific portion of the tube called the ampullar-isthmic junction, it rests for another thirty hours. Fertilization (sperm union with the egg) occurs in this portion of the tube. The fertilized egg then begins a rapid descent to the uterus. The period of rest in the tube appears to be necessary for full development of the fertilized egg and preparation of the uterus for receipt of the egg. Defects in the fallopian tube may impair transport and increase the risk of tubal (ectopic) pregnancy.
Fertilization and Embryo Development
Following ovulation, the egg is capable of fertilization for only 12-24 hours. Contact between the egg and sperm is random. A membrane (shell) surrounding the egg, the zona pellucida, has two major functions in fertilization. First, the zona pellucida contains sperm receptors which are specific for human sperm. Second, once the membrane has been penetrated by the sperm, it becomes impermeable to penetration by other sperm. Following penetration, a series of events set the stage for the first cell division. The single-cell embryo is called a "zygote." Over the course of the next seven days, the human embryo undergoes multiple cell divisions in a process called mitosis. At the end of this transition period, the embryo becomes a mass of very organized cells called a blastocyst. As women get older, it is now believed, this process of early embryo development is increasingly impaired due to diminishing egg quality.
Implantation
Once the embryo reaches the blastocyst stage (approximately five to six days after fertilization), it hatches out of its zona pellucida (shell) and begins the process of implantation. In nature, 50% of all fertilized eggs are lost before a woman's missed menses. So, too, in the in vitro fertilization (IVF) process an embryo may begin to develop but not make it to the blastocyst stage (the first stage where those cells destined to become the fetus separate from those which will become the placenta). The blastocyst may implant but not grow or the blastocyst may grow and still cease development before the two week time at which a pregnancy can be detected. The receptivity of the uterus and the health of the embryo are important for the implantation process.
Timeline of Getting Pregnant
You calculate your menstrual cycle from the first day of menstrual bleeding to the start of the next first day of menstrual bleeding. Most menstrual cycles are around 28 days long. The exact time you ovulate varies depending on how long your menstrual cycle is.
The process of getting pregnant in a 28-day menstrual cycle is: Day one: First day of your period. Around day 14: Ovulation occurs. Within 24 hours of ovulation: Sperm fertilizes an egg (conception occurs).
What are my chances of conceiving?
Just because an egg and sperm are near each other doesn't mean conception will happen. In general, conception only happens 25% to 30% of the time. This percentage decreases once you reach age 35.
How does conception work with IVF?
Conception still works the same way — sperm must fertilize an egg. However, with in vitro fertilization (IVF), sperm fertilizes an egg in a lab. An egg, either from the intended parent or a donor, is mixed with sperm from a parent or donor. Conception happens when sperm fertilizes the egg. Once conception occurs, your provider places the created embryo inside the uterus that will carry the pregnancy for implantation.
When does conception happen?
Conception occurs between 12 and 24 hours after ovulation. It’s sometimes hard to pinpoint ovulation, so using ovulation predictor kits or tracking your menstrual cycle on a calendar may be helpful.
The two biggest factors in conception are:
- The timing of sexual intercourse with ovulation.
- Egg and sperm health.
When should I have sex to conceive?
Conception can happen after unprotected sex as early as five days before ovulation. This is because some sperm can live that long inside female reproductive organs.
If you’re trying to conceive, the best times to have sex are:
- In the three days before ovulation: In this scenario, sperm will be “waiting” for the egg to come down the fallopian tube.
- At ovulation or within 24 hours of ovulating: Your egg lives for only 24 hours, so if you have unprotected sex during this time, your egg may end up “waiting” for sperm to reach it, or they may run into each other in your fallopian tubes.
What things prevent conception from happening?
Certain health conditions may affect your ability to conceive. Just because the sperm and egg meet doesn't mean fertilization will occur. Some of the most common factors are:
- Anovulation (you’re not ovulating).
- Low sperm count or issues with sperm motility (how sperm move).
- A blockage in the testicles, ovaries or fallopian tubes.
- Decreasing amount of quality eggs and quality sperm (usually related to aging).
Can you feel conception?
Not usually. You may notice signs that you've ovulated, such as changes in your cervical mucus or basal body temperature. However, most people don't feel fertilization. You may feel a dull ache or experience light spotting several days after conception. This could be from the fertilized egg implanting in your uterus.
When do you start feeling pregnant?
How long it takes to “feel” pregnant varies. Some people may start to feel pregnant shortly after conception, while others don’t have any pregnancy symptoms for weeks after a positive test. Common signs of pregnancy are:
- A missed period.
- Frequent urination.
- Feeling tired. Nausea.
- Sore or swollen breasts.
- Spotting (light vaginal bleeding).
- Headaches.
- Mood swings.
Take a home pregnancy test if you have any of the above symptoms and think there’s a chance you’re pregnant. Pregnancy Test Kits are available on Thexco Health. Your healthcare provider can order a blood test to confirm pregnancy.
How long after conception will my pregnancy test be positive?
It can take between 11 and 14 days after conception to get a positive pregnancy test. At-home pregnancy tests check for human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), a hormone released by the placenta. Your pee must have enough hCG to get a positive pregnancy test. However, your healthcare provider can check for hCG in your blood sooner — around 10 days after conception.
Conception is when sperm fertilizes an egg. It’s one of the many critical steps in getting pregnant. Conceiving a child is a complex process dependent on lots of factors. Being unable to conceive is a common problem, and there are lots of resources available to help you.
If you’re struggling with conceiving, Contact Thexco Health Here to Book an Appointment with a healthcare professional and or Request a Callback.